阿里云优惠活动,点击链接进行购买: 一年仅需96.9元即可以购买服务器~
腾讯云优惠活动, 点击链接进行购买一年仅需99元
腾讯云限时开团活动, 点击链接进行购买一年仅需95元
前段实践了一下 Node 的 C++ 编写,对于底层的编程实践是每个程序员心中所向往的圣地。由于接触的 Node C++ 的时间比较少,可能还无法完全理解其中的精髓,但是本文只记录自己的一个实践。
先来看看 Node Addons 在整个模块中的所处的位置。
Addons 是用 C ++编写的动态链接的共享对象。 require() 函数可以将 Addons 加载为普通的 Node.js 模块,Addons 提供 JavaScript 和 C / C ++ 库之间的接口。
在现代,Node 官方推荐的方式为以下三种, 插件编写历史可以查看 《从暴力到 NAN 再到 NAPI——Node.js 原生模块开发方式变迁》 (opens new window)
1.NAN (一个充满宏和实用工具的头文件,使 Node.js 的插件开发在 0.8、0.10、0.12、1、2、3、4、5、6、7、8、9、10、11、12 和 13 版本之间更容易。)
2.NAPI (N-API(在字母中发音为 N,后跟 API)是用于构建本机插件的 API。 它独立于底层 JavaScript 运行时(例如 V8),并作为 Node.js 本身的一部分进行维护。)
3.直接使用内部的 V8、Libuv 和 Node.js 库(需要掌握 V8, libuv, Node 原生库方法,Node.js 包括其他静态链接的库,包括 OpenSSL )
如果你不使用 NAPI 的未公开的 API,优先使用 NAPI 进行插件开发。
NAN 和 NAPI 的区别
NAN 解决了混乱的 C++原生模块,不再让一个模块只能被若干个 Node 版本使用,而提出使用宏定义来解决这个问题,所以说 NAN 是一大堆宏定义,兼容各种 Node 版本的宏定义。做到了一次编写,到处编译。
而这种设计模式还是依然有缺点,那就是多次编译,也就是说你写的插件如果到了更高的 Node 版本,还是需要再次编译,因此有来额 NAPI,它旨在使 Addons 与基础 JavaScript 引擎的更改保持隔离,并使为一个主要版本编译的模块可以在 Node 的更高主要版本上运行,而无需重新编译。
随着时代的前进,我当然选择了最新的 NAPI 进行实践,虽然最新的 API 的封装地非常友好,看起来编写已经不是那么复杂,但是对于深入理解 V8 以及 Node 原生模块来说,提升没有从更下层编写来的大。不过,这也不妨碍我们的学习,我们先来看看上层的实践,快速搭建应用,然后慢慢地去理解整个过程,也是一个非常好的方式。
还有一点就是,N-API 是一个 C API,确保 ABI (opens new window) 跨 Node.js 版本和不同编译器级别的稳定性。C++ API 更容易使用。为了支持使用 C++,该项目维护了一个名为 node-addon-api (opens new window) 的 C++ 包装器模块。因此我们会使用进行包装后的 node-addon-api 来进行开发。
本文使用的环境
> g++ --verison
Configured with: --prefix=/Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer/usr --with-gxx-include-dir=/Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer/Platforms/MacOSX.platform/Developer/SDKs/MacOSX10.14.sdk/usr/include/c++/4.2.1
Apple LLVM version 10.0.0 (clang-1000.11.45.5)
Target: x86_64-apple-darwin18.0.0
Thread model: posix
InstalledDir: /Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer/Toolchains/XcodeDefault.xctoolchain/usr/bin
> node -v
v10.16.0
> sw_vers
ProductName: Mac OS X
ProductVersion: 10.14
ProductName: Mac OS X
ProductVersion: 10.14
BuildVersion: 18A391
既然要实现一个 LRU,那必须对这个算法有一个初步的了解。LRU(Least Recently Used 意思为 最近最少使用)
以内存访问为例解释缓存的工作原理。假设缓存的大小固定,初始状态为空。每发生一次读内存操作,首先查找待读取的数据是否存在于缓存中,若是,则缓存命中,返回数据;若否,则缓存未命中,从内存中读取数据,并把该数据添加到缓存中。向缓存添加数据时,如果缓存已满,则需要删除访问时间最早的那条数据,这种更新缓存的方法就叫做 LRU。
可以用以下图来进行演示说明,假设我们最多只能开 3 个应用,第一次我们开了知乎,然后知乎为最近使用,第二次,我们点击了 qq 音乐,然后我们的 qq 音乐会成为最近使用的应用。最后我们又打开了美团,此时爱奇艺应用被删除,美团成为最近使用的应用。
为了实现 LRU,我们需要保证他的读写性能。理想状态为在 O(1) 的时间内读取或者更新一条数据。通过这个现象我们可以使用 HashMap 来实现这个存储,根据键值访问可以达到 O(1) 的速度。现在还差更新数据,由于我们需要确定最早的那条数据,所以我们需要遍历所有数据。
首先我们可以想到链表是一种有顺序的数据结构,其次由于我们被访问的数据有可能为非首尾结点,所以我们需要使用双向链表,来保证我们可以从中间任意结点修改链表。
现在我们确定了我们的数据结构为 HashMap + 双向链表。
我用图来描述一下整个过程,假设我们总长度为 4。(左侧为双向链表,右侧为 HashMap)
由于一开始对 Node Addons 不太了解,因此先写了一个 c++ 版本,方便逻辑的调试。
list.h
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Node {
public:
string data;
Node *next;
Node *prev;
Node(string da, Node *p = NULL) {
this->data = da;
this->next = p;
}
};
class List {
private:
Node *head, *tail;
int position;
int count = 0;
int maxCount = 200;
unordered_map <string, string> cachemap;
public:
List() {
head = tail = NULL;
};
void SetMax(int da);
void Print();
void Insert (string da, string value);
void Delete(string da);
void Search(string da);
};
list.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "list.hpp"
#include <string>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
void List::SetMax(int da) {
maxCount = da;
}
void List::Print() {
Node *p = head;
while(p != NULL) {
string key = p->data;
unordered_map<string ,string >::iterator l_it;
l_it = this->cachemap.find(key);
if(l_it != this->cachemap.end()) {
cout << l_it->second << endl;
}
p = p->next;
}
}
void List::Delete(string da) {
Node *p = head, *q = head;
if(p == NULL) {
cout << "can't find value %d" << da << endl;
return;
}
string value = "";
while (p != NULL) {
if(p->data == da) {
value = da;
break;
}
q = p;
p = p->next;
}
if(p == NULL) {
cout << "del can't find value " << da << endl;
} else {
q->next = p->next;
cout << "del value " << da << endl;
}
}
void List::Insert(string da, string value) {
if(count >= maxCount) {
tail->prev->next = NULL;
tail = tail->prev;
Node *p = new Node(da);
cachemap.insert(pair<string, string>(da, value));
p->next = head;
head->prev = p;
head = p;
head->prev = NULL;
return;
}
if(head == NULL) {
head = tail = new Node(da);
cachemap.insert(pair<string, string>(da, value));
head->next = NULL;
head->prev = NULL;
tail->next = NULL;
tail->prev = NULL;
} else {
Node *p = new Node(da);
cachemap.insert(pair<string, string>(da, value));
head->prev = p;
p->next = head;
p->prev = NULL;
head = p;
}
count++;
}
void List::Search(string da) {
Node *p = head;
if(p == NULL) {
cout << "can't find" << endl;
return;
}
int count = -1;
int i = 0;
while( p!= NULL ) {
if(p->data == da) {
count = i;
break;
}
p = p->next;
i ++;
}
if(count != -1) {
p->prev->next = p->next;
if(p->next != NULL) {
p->next->prev = p->prev;
}
p->next = head;
p->prev = NULL;
head->prev = p;
head = p;
unordered_map<string ,string >::iterator l_it;
l_it = this->cachemap.find(da);
if(l_it == this->cachemap.end()) {
cout << "can't find key " << da << endl;
} else {
cout << "find value is " << l_it->second << endl;
}
} else {
cout << "can't find key" << da << endl;
}
}
1.设置缓存长度
2.获取缓存长度
3.打印所有缓存数据
4.插入缓存数据
5.获取缓存数据
├── binding.gyp // 编译配置
├── package.json
├── src
│ ├── bingding.cc // 声明模块导出
│ ├── list.cc // 主入口
│ └── list.h // 头文件声明
└── index.js // 主文件入口
npm init -y
{
"targets": [
{
"target_name": "LRU_node_addon",
"cflags!": ["-fno-exceptions"],
"cflags_cc!": ["-fno-exceptions"],
"sources": ["./src/bingding.cc", "./src/list.cc"],
"include_dirs": ["<!@(node -p \"require('node-addon-api').include\")"],
"defines": ["NAPI_DISABLE_CPP_EXCEPTIONS"]
}
]
}
npm i bindings node-addon-api -S
注: bingding 是用来引入 c++ 模块,node-addon-api 是 NAPI 的 c++ 封装
NAN 模块的初始化是交给 Node.js 提供的宏来实现的:
NODE_MODULE(addon, init)
而 N-API 使用自己的宏定义(NAPI_MODULE),因为我们使用node-addon-api,所以它也对这个宏定义包裹成下面这个了:
NODE_API_MODULE(addon, Init)
编写我们的导出模块 binding.cc
#include <napi.h>
#include "list.h"
Napi::Object InitAll(Napi::Env env, Napi::Object exports) {
return List::Init(env, exports);
}
NODE_API_MODULE(NODE_GYP_MODULE_NAME, InitAll)
做完了上述的准备工作,就可以开始改造我们的主逻辑,转化为 Node Addons ,主要还是因为 Node 无法直接调用 c++, 因此需要经过包装,我们的主要任务就是将 c++ 的类型包装为 v8 的类型,这一部分 node-addon-api 已经封装好,我们直接使用即可。(主要我写的这个比较简单,没有用到特别复杂的特性,主要作为一个小小的实践。)
修改声明文件
这里主要是对函数的返回值以及入参进行修改。
入参: Napi::CallbackInfo 主要为 js 调用时传入的请求参数。
返回值: Napi::Value是 js 值的 C ++表示。
...
class List : public Napi::ObjectWrap<List>{
private:
Node *head, *tail;
int count = 0;
int maxCount = 200;
unordered_map <string, string> cachemap;
public:
static Napi::Object Init(Napi::Env env, Napi::Object exports); // 初始化
static Napi::FunctionReference constructor; // 创建 FunctionReference ,防止被垃圾回收
List(const Napi::CallbackInfo& info); // 类构造函数
void SetMax(const Napi::CallbackInfo& info);
Napi::Value getMax(const Napi::CallbackInfo& info);
Napi::Value Print(const Napi::CallbackInfo& info);
void Insert (const Napi::CallbackInfo& info);
Napi::Value Search(const Napi::CallbackInfo& info);
}
...
设置缓存长度
通过对 info 参数来获取 js 传入的参数。增加一些类型判断,如果非数字则想 js 抛出错误。
void List::SetMax(const Napi::CallbackInfo& info) {
int length = info.Length();
Napi::Env env = info.Env();
if (length <= 0 || !info[0].IsNumber()) {
Napi::TypeError::New(env, "Number expected").ThrowAsJavaScriptException();
}
Napi::Number value = info[0].As<Napi::Number>();
int cvalue = value.Int32Value();
if(cvalue < 10) {
Napi::TypeError::New(env, "min count is 10").ThrowAsJavaScriptException();
}
this->maxCount = cvalue;
}
获取缓存长度
修改返回值为 Napi::Value 统一方式。
Napi::Value List::getMax(const Napi::CallbackInfo& info) {
int num = this->maxCount;
return Napi::Number::New(info.Env(), num);
}
打印所有缓存数据
通过对链表的迭代,获取所有数据并创建 Napi::Array 来进行存储。最后返回。
Napi::Value List::Print(const Napi::CallbackInfo& info) {
// array https://github.com/nodejs/node-addon-api/issues/423
Node *p = this->head;
Napi::Array arr = Napi::Array::New(info.Env(), this->count);
int i = 0;
while(p != NULL) {
string key = p->data;
unordered_map<string ,string >::iterator l_it;
l_it = this->cachemap.find(key);
if(l_it != this->cachemap.end()) {
arr[i] = Napi::String::New(info.Env(), l_it->second);
}
i++;
p = p->next;
}
return arr;
}
插入缓存数据
修改点也比较少,主要就是
info[0].As<Napi::String>()
info[1].As<Napi::String>()
用来获取 js 传入的参数,其他就是正常的数据类型改造。
void List::Insert(const Napi::CallbackInfo& info) {
int length = info.Length();
Napi::Env env = info.Env();
if (length <= 1 || !info[0].IsString() || !info[1].IsString()) {
Napi::TypeError::New(env, "key and value expected").ThrowAsJavaScriptException();
}
Napi::String key = info[0].As<Napi::String>();
Napi::String value = info[1].As<Napi::String>();
string da = key.ToString();
if(this->count >= this->maxCount) {
this->tail->prev->next = NULL;
this->tail = this->tail->prev;
Node *p = new Node(da);
this->cachemap.insert(std::pair<string, string>(da, value));
p->next = this->head;
this->head->prev = p;
this->head = p;
this->head->prev = NULL;
return;
}
if(this->head == NULL) {
this->head = this->tail = new Node(da);
this->cachemap.insert(std::pair<string, string>(da, value));
this->head->next = NULL;
this->head->prev = NULL;
this->tail->next = NULL;
this->tail->prev = NULL;
} else {
Node *p = new Node(da);
this->cachemap.insert(std::pair<string, string>(da, value));
this->head->prev = p;
p->next = this->head;
p->prev = NULL;
this->head = p;
}
this->count++;
}
获取缓存数据
获取到 js 传入 key 的后,通过循环链表查找是否存在改 key值,如果存在就去 map 中获取 value
Napi::Value List::Search(const Napi::CallbackInfo& info) {
int length = info.Length();
Napi::Env env = info.Env();
if (length <= 0 || !info[0].IsString()) {
Napi::TypeError::New(env, "String expected").ThrowAsJavaScriptException();
}
Napi::String value = info[0].As<Napi::String>();
string da = value.ToString();
Node *p = this->head;
if(p == NULL) {
return Napi::String::New(info.Env(), INITVALUE);
}
int count = -1;
int i = 0;
while( p!= NULL) {
if(p->data == da) {
count = i;
break;
}
p = p->next;
i ++;
}
if(count != -1) {
p->prev->next = p->next;
if(p->next != NULL) {
p->next->prev = p->prev;
}
p->next = this->head;
p->prev = NULL;
this->head->prev = p;
this->head = p;
unordered_map<string ,string >::iterator l_it;
l_it = this->cachemap.find(da);
if(l_it == this->cachemap.end()) {
return Napi::String::New(info.Env(), INITVALUE);
} else {
return Napi::String::New(info.Env(), l_it->second);
}
} else {
return Napi::String::New(info.Env(), INITVALUE);
}
return Napi::String::New(info.Env(), INITVALUE);
}
打包模式
node-gyp configure && node-gyp build
调试模式
node-gyp configure && node-gyp build --debug
通过 node-gyp 编译后, 会出现对应的 build 目录,打包模式 build 下面会有 一个 Release 目录,调试模式则是 Debug 目录。
运行测试文件 test.js
const List = require("bindings")("LRU_node_addon").List;
const list = new List();
list.SetMax(10);
list.Insert("10", "hello");
list.Insert("11", "world");
list.Insert("12", "hi1");
list.Insert("13", "hi2");
list.Insert("14", "hi3");
list.Insert("15", "hi4");
list.Insert("16", "hi5");
list.Insert("17", "hi6");
list.Insert("18", "hi7");
list.Insert("19", "hi8");
list.Insert("20", "hi9");
list.Insert("21", "hi10");
console.log(list.Search("10"));
console.log(list.Print());
output
由于设置缓存最长长度为 10,因为已经查找不到 "10" 这个 key 了。
>
>[ 'hi10',
'hi9',
'hi8',
'hi7',
'hi6',
'hi5',
'hi4',
'hi3',
'hi2',
'hi1' ]
以下都是基于 vscode 进行调试。
调试 Node
创建 .vscode/launch.json, 添加以下配置。preLaunchTask 为调试前运行的命令,保证每次调试的都是 最近的 c++ 扩展代码。(也可以去除这个文件)
{
"type": "node",
"request": "launch",
"name": "JS Debug Build",
"console": "integratedTerminal",
"program": "${workspaceFolder}/test.js",
"preLaunchTask": "npm: build:debug"
}
然后打上两个断点,在调试面板 找到 JS Debug Build。单击运行,就可以看到效果了。
调试 c++
vscode 默认不支持 c/c++ 的调试,先安装 c/c++ 插件。
添加配置
{
"name": "(lldb) Launch",
"type": "cppdbg",
"request": "launch",
"program": "/Users/huayifeng/.nvm/versions/node/v10.16.0/bin/node",
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}",
"args": [
"${workspaceFolder}/test.js"
],
"MIMode": "lldb",
},
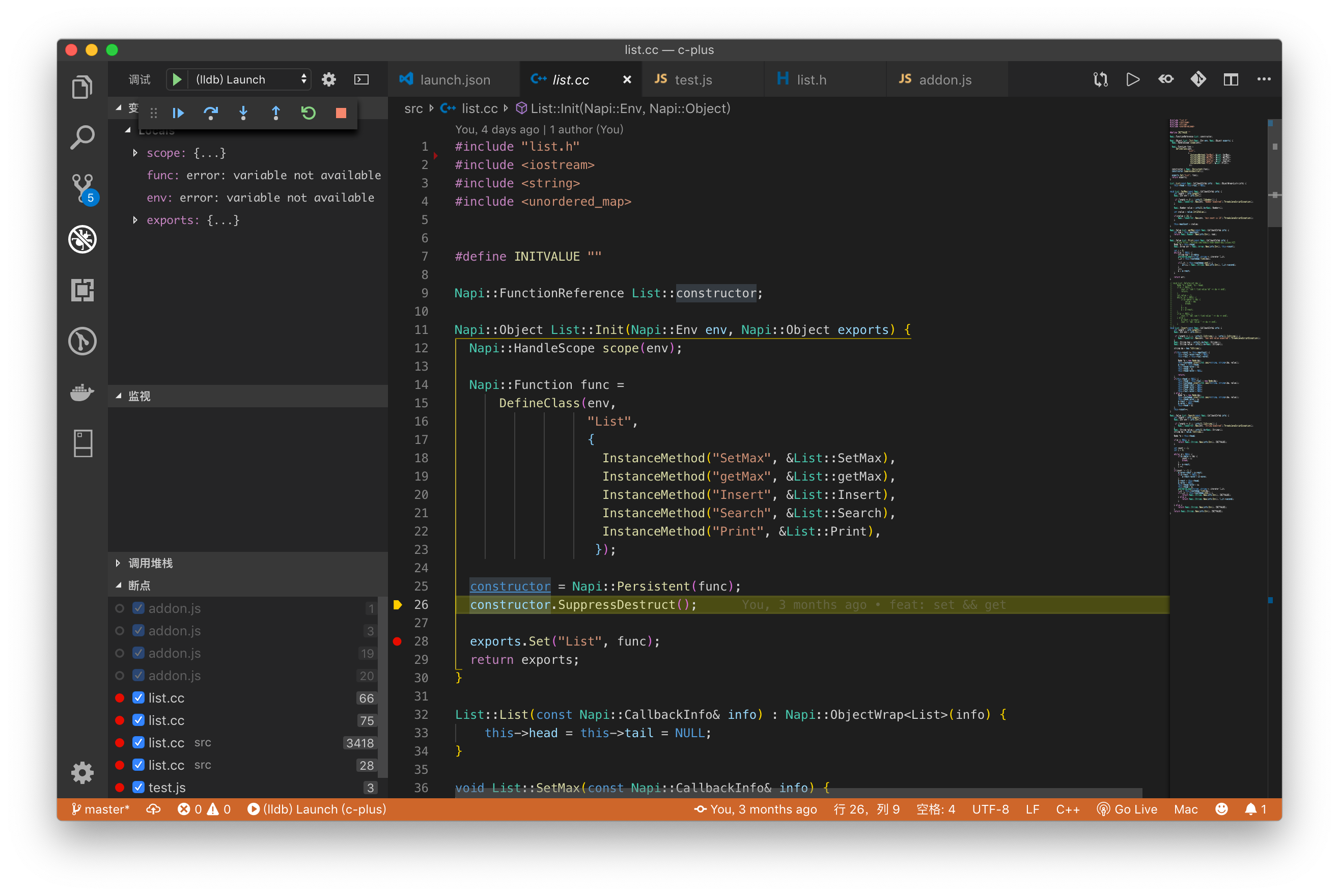
给 list.cc 打上断点。在调试面板 找到 (lldb) Launch。单击运行,就可以看到效果了。
包版本管理
根据语义化版本管理(semantic-version)https://docs.npmjs.com/about-semantic-versioning
这里可以看我的另一个包 https://github.com/zerolty/auto-version 帮助你更好地管理版本。
为了帮助开发人员管理好依赖代码,我们建议你从 1.0.0 作为初始版本进行迭代。
| Code status | Stage | Rule | Example version |
|---|---|---|---|
| First release | New product | Start with 1.0.0 | 1.0.0 |
| Backward compatible bug fixes | Patch release | Increment the third digit | 1.0.1 |
| Backward compatible new features | Minor release | Increment the middle digit and reset last digit to zero | 1.1.0 |
| Changes that break backward compatibility | Major release | Increment the first digit and reset middle and last digits to zero | 2.0.0 |
上述表格摘自 npm ,懒得翻译了。。。
定义入口
package.json
{
"name": "lru-node-addon",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"scripts": {
"build:debug": "node-gyp configure && node-gyp build --debug",
"build:release": "node-gyp configure && node-gyp build"
},
"main": "index.js",
"files": ["src", "index.js", "binding.gyp"],
"gypfile": true,
"dependencies": {
"bindings": "~1.2.1",
"node-addon-api": "^1.0.0"
}
}
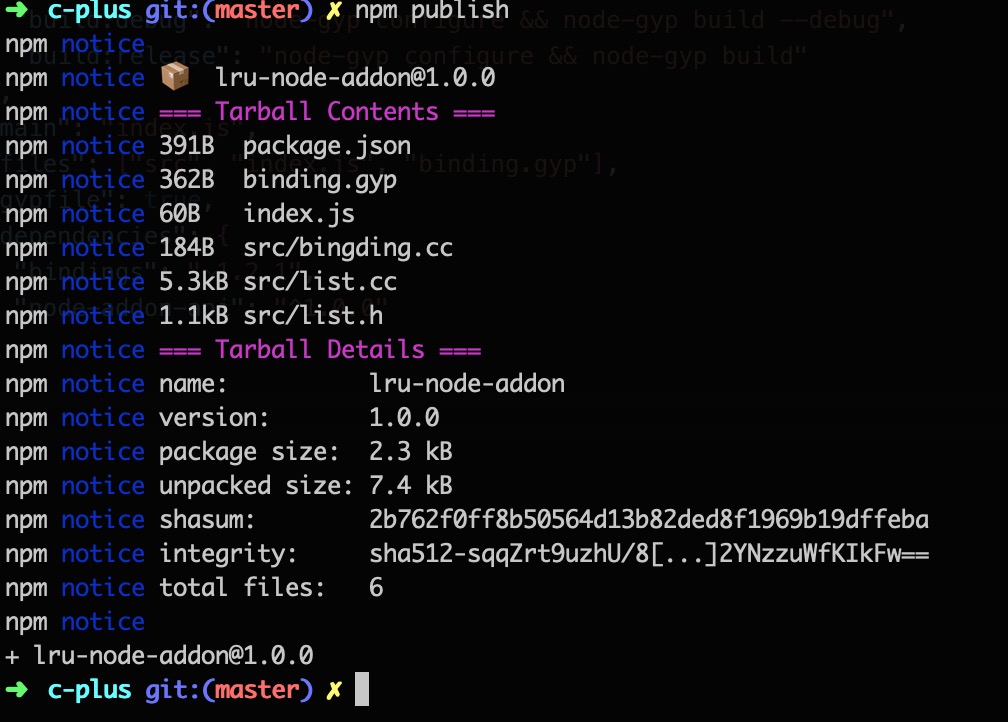
发布
npm publish
时间
| 100 | 1000 | 10000 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Node | 1.828ms | 3.264ms | 42.393ms |
| Addon | 0.605ms | 5.953ms | 525.639ms |
内存使用(heapUsed)
| 100 | 1000 | 10000 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Node | 3.96MB | 4.46MB | 6.72MB |
| Addon | 3.90MB | 4.23MB | 5.45MB |
测试发现随着数量的增加。用原生的 node 速度更快一些,但是内存占用更多。。 。这个回头再写一篇研究一下。还没有具体分析。。。
以上所有示例的 github 地址
https://github.com/hua1995116/LRU-node-addon
https://juejin.im/post/5de484bef265da05ef59feb5
https://www.jianshu.com/p/b1ab4a170c3c
https://cnodejs.org/topic/5957626dacfce9295ba072e0
https://github.com/nodejs/node-addon-api
https://gyp.gsrc.io/docs/UserDocumentation.md
https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/opensource/os-cn-v8engine/
https://nodejs.org/dist/latest/docs/api/n-api.html
